Page 115 - ToTheTop2030_2_SE
P. 115
Grammar Reference
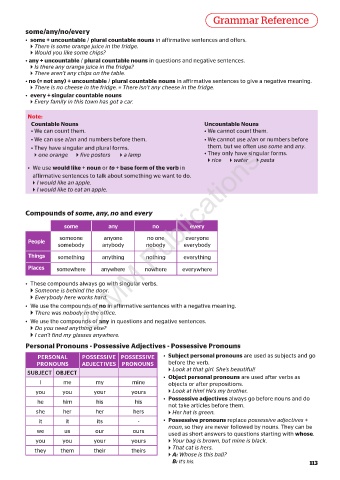
some/any/no/every
• some + uncountable / plural countable nouns in affirmative sentences and offers.
There is some orange juice in the fridge.
Would you like some chips?
• any + uncountable / plural countable nouns in questions and negative sentences.
Is there any orange juice in the fridge?
There aren’t any chips on the table.
• no (= not any) + uncountable / plural countable nouns in affirmative sentences to give a negative meaning.
There is no cheese in the fridge. = There isn’t any cheese in the fridge.
• every + singular countable nouns
Every family in this town has got a car.
Note:
Countable Nouns Uncountable Nouns
• We can count them. • We cannot count them.
• We can use a/an and numbers before them. • We cannot use a/an or numbers before
• They have singular and plural forms. them, but we often use some and any.
one orange five posters a lamp • They only have singular forms.
rice water pasta
• We use would like + noun or to + base form of the verb in
affirmative sentences to talk about something we want to do.
I would like an apple.
I would like to eat an apple.
Compounds of some, any, no and every
some any no every
no one
anyone
someone © MM Publications
everyone
People
somebody anybody nobody everybody
Things something anything nothing everything
Places somewhere anywhere nowhere everywhere
• These compounds always go with singular verbs.
Someone is behind the door.
Everybody here works hard.
• We use the compounds of no in affirmative sentences with a negative meaning.
There was nobody in the office.
• We use the compounds of any in questions and negative sentences.
Do you need anything else?
I can’t find my glasses anywhere.
Personal Pronouns - Possessive Adjectives - Possessive Pronouns
PERSONAL POSSESSIVE POSSESSIVE • Subject personal pronouns are used as subjects and go
PRONOUNS ADJECTIVES PRONOUNS before the verb.
Look at that girl. She’s beautiful!
SUBJECT OBJECT
• Object personal pronouns are used after verbs as
I me my mine objects or after prepositions.
you you your yours Look at him! He’s my brother.
• Possessive adjectives always go before nouns and do
he him his his
not take articles before them.
she her her hers Her hat is green.
it it its - • Possessive pronouns replace possessive adjectives +
noun, so they are never followed by nouns. They can be
we us our ours
used as short answers to questions starting with whose.
you you your yours Your bag is brown, but mine is black.
That cat is hers.
they them their theirs
A: Whose is this ball?
B: It’s his. 113
5/7/2023 11:18:01 πµ
ToTheTop2030_SRB_2_SB.indb 113 5/7/2023 11:18:01 πµ
ToTheTop2030_SRB_2_SB.indb 113