Page 133 - ToTheTop2030_1_SE
P. 133
Grammar Reference
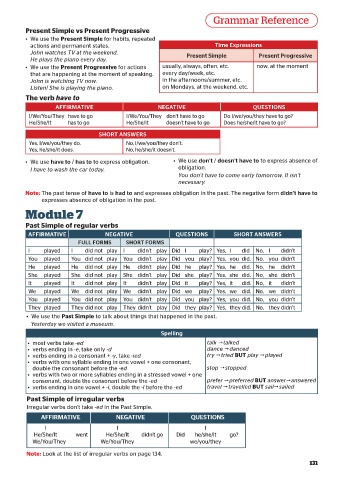
Present Simple vs Present Progressive
• We use the Present Simple for habits, repeated
actions and permanent states. Time Expressions
John watches TV at the weekend. Present Simple Present Progressive
He plays the piano every day.
• We use the Present Progressive for actions usually, always, often, etc. now, at the moment
that are happening at the moment of speaking. every day/week, etc.
John is watching TV now. in the afternoons/summer, etc.
Listen! She is playing the piano. on Mondays, at the weekend, etc.
The verb have to
AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE QUESTIONS
I/We/You/They have to go I/We/You/They don’t have to go Do I/we/you/they have to go?
He/She/It has to go He/She/It doesn’t have to go Does he/she/it have to go?
SHORT ANSWERS
Yes, I/we/you/they do. No, I/we/you/they don’t.
Yes, he/she/it does. No, he/she/it doesn’t.
• We use have to / has to to express obligation. • We use don’t / doesn’t have to to express absence of
I have to wash the car today. obligation.
You don’t have to come early tomorrow. It isn’t
necessary.
Note: The past tense of have to is had to and expresses obligation in the past. The negative form didn’t have to
expresses absence of obligation in the past.
Module 7
Past Simple of regular verbs
AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE QUESTIONS SHORT ANSWERS
FULL FORMS SHORT FORMS
I played I did not play I didn’t play Did I play? Yes, I did No, I didn’t
You played You did not play You didn’t play Did you play? Yes, you did. No, you didn’t
He played He did not play He didn’t play Did he play? Yes, he did. No, he didn’t
She played She did not play She didn’t play Did she play? Yes, she did. No, she didn’t
It played It did not play It didn’t play Did it play? Yes, it did. No, it didn’t
We played We did not play We didn’t play Did we play? Yes, we did. No, we didn’t
You played You did not play You didn’t play Did you play? Yes, you did. No, you didn’t
They played They did not play They didn’t play Did they play? Yes, they did. No, they didn’t
• We use the Past Simple to talk about things that happened in the past.
Yesterday we visited a museum.
Spelling
• most verbs take -ed talk talked
• verbs ending in -e, take only -d dance danced
• verbs ending in a consonant + -y, take -ied try tried BUT play played
• verbs with one syllable ending in one vowel + one consonant,
double the consonant before the -ed stop stopped
• verbs with two or more syllables ending in a stressed vowel + one
consonant, double the consonant before the -ed prefer preferred BUT answeranswered
• verbs ending in one vowel + -l, double the -l before the -ed travel travelled BUT sailsailed
Past Simple of irregular verbs
Irregular verbs don't take -ed in the Past Simple.
AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE QUESTIONS
I I I
He/She/It went He/She/It didn't go Did he/she/it go?
We/You/They We/You/They we/you/they
Note: Look at the list of irregular verbs on page 134.
131
12/9/2022 4:08:26 µµ
Book_To the Top Plus_SRB_1.indb 131
Book_To the Top Plus_SRB_1.indb 131 12/9/2022 4:08:26 µµ