Page 120 - TTTP_2_SB_SE
P. 120
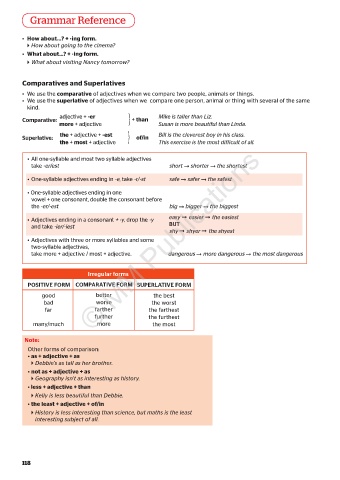
Grammar Reference
• How about...? + -ing form.
How about going to the cinema?
• What about…? + -ing form.
What about visiting Nancy tomorrow?
Comparatives and Superlatives
• We use the comparative of adjectives when we compare two people, animals or things.
• We use the superlative of adjectives when we compare one person, animal or thing with several of the same
kind.
adjective + -er } Mike is taller than Liz.
Comparative: + than
more + adjective Susan is more beautiful than Linda.
the + adjective + -est } Bill is the cleverest boy in his class.
Superlative: of/in
the + most + adjective This exercise is the most difficult of all.
• All one-syllable and most two syllable adjectives
take -er/est short Þ shorter Þ the shortest
• One-syllable adjectives ending in -e, take -r/-st safe Þ safer Þ the safest
• One-syllable adjectives ending in one
vowel + one consonant, double the consonant before
the -er/-est big Þ bigger Þ the biggest
• Adjectives ending in a consonant + -y, drop the -y easy Þ easier Þ the easiest
BUT
and take -ier/-iest farther MM Publications
shy Þ shyer Þ the shyest
• Adjectives with three or more syllables and some
two-syllable adjectives,
take more + adjective / most + adjective. dangerous Þ more dangerous Þ the most dangerous
Irregular forms
PoSITIve form ComPArATIve form SUPerLATIve form
good better the best
bad worse the worst
far © further the farthest
the most
many/much more the furthest
Note:
Other forms of comparison:
• as + adjective + as
Debbie’s as tall as her brother.
• not as + adjective + as
Geography isn’t as interesting as history.
• less + adjective + than
Kelly is less beautiful than Debbie.
• the least + adjective + of/in
History is less interesting than science, but maths is the least
interesting subject of all.
118
To the Top_Plus2_SB_GrammarReference.indd 118 5/12/2018 9:52:34 πµ