Page 114 - TTTP_2_SB_SE
P. 114
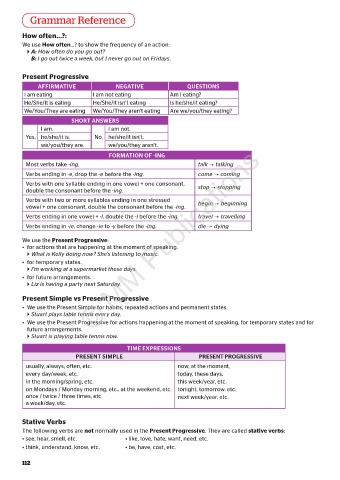
Grammar Reference
How often...?:
We use How often...? to show the frequency of an action:
A: How often do you go out?
B: I go out twice a week, but I never go out on Fridays.
Present Progressive
AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE QUESTIONS
I am eating I am not eating Am I eating?
He/She/It is eating He/She/It isn’t eating Is he/she/it eating?
We/You/They are eating We/You/They aren’t eating Are we/you/they eating?
SHORT ANSWERS
I am. I am not.
Yes, he/she/it is. No, he/she/it isn’t.
future arrangements. © MM Publications
we/you/they are. we/you/they aren’t.
FORMATION OF -ING
Most verbs take -ing. talk talking
Verbs ending in -e, drop the -e before the -ing. come coming
Verbs with one syllable ending in one vowel + one consonant, stop stopping
double the consonant before the -ing.
Verbs with two or more syllables ending in one stressed begin beginning
vowel + one consonant, double the consonant before the -ing.
Verbs ending in one vowel + -l, double the -l before the -ing. travel travelling
Verbs ending in -ie, change -ie to -y before the -ing. die dying
We use the Present Progressive:
• for actions that are happening at the moment of speaking.
What is Kelly doing now? She’s listening to music.
• for temporary states.
I’m working at a supermarket these days.
• for future arrangements.
Liz is having a party next Saturday.
Present Simple vs Present Progressive
• We use the Present Simple for habits, repeated actions and permanent states.
Stuart plays table tennis every day.
• We use the Present Progressive for actions happening at the moment of speaking, for temporary states and for
Stuart is playing table tennis now.
TIME EXPRESSIONS
PRESENT SIMPLE PRESENT PROGRESSIVE
usually, always, often, etc. now, at the moment,
every day/week, etc. today, these days,
in the morning/spring, etc. this week/year, etc.
on Mondays / Monday morning, etc., at the weekend, etc. tonight, tomorrow, etc.
once / twice / three times, etc. next week/year, etc.
a week/day, etc.
Stative Verbs
The following verbs are not normally used in the Present Progressive. They are called stative verbs:
• see, hear, smell, etc. • like, love, hate, want, need, etc.
• think, understand, know, etc. • be, have, cost, etc.
112
To the Top_Plus2_SB_GrammarReference.indd 112 11/23/2018 4:27:40 PM