Page 113 - GTTT_4_SB_SE
P. 113
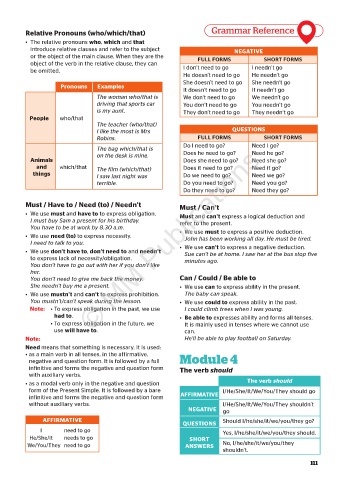
Relative Pronouns (who/which/that) Grammar Reference
• The relative pronouns who, which and that
introduce relative clauses and refer to the subject NEGATIVE
or the object of the main clause. When they are the FULL FORMS SHORT FORMS
object of the verb in the relative clause, they can
be omitted. I don’t need to go I needn’t go
He doesn’t need to go He needn’t go
She doesn’t need to go She needn’t go
Pronouns Examples
It doesn’t need to go It needn’t go
The woman who/that is We don’t need to go We needn’t go
driving that sports car You don’t need to go You needn’t go
is my aunt. They don’t need to go They needn’t go
People who/that
The teacher (who/that)
I like the most is Mrs QUESTIONS
Robins. FULL FORMS SHORT FORMS
use will have to. © MM Publications
Do I need to go? Need I go?
The bag which/that is
on the desk is mine. Does he need to go? Need he go?
Animals Does she need to go? Need she go?
and which/that The film (which/that) Does it need to go? Need it go?
things I saw last night was Do we need to go? Need we go?
terrible. Do you need to go? Need you go?
Do they need to go? Need they go?
Must / Have to / Need (to) / Needn’t Must / Can’t
• We use must and have to to express obligation. Must and can’t express a logical deduction and
I must buy Sam a present for his birthday. refer to the present.
You have to be at work by 8.30 a.m.
• We use need (to) to express necessity. • We use must to express a positive deduction.
John has been working all day. He must be tired.
I need to talk to you.
• We use can’t to express a negative deduction.
• We use don’t have to, don’t need to and needn’t Sue can’t be at home. I saw her at the bus stop five
to express lack of necessity/obligation. minutes ago.
You don’t have to go out with her if you don’t like
her.
You don’t need to give me back the money. Can / Could / Be able to
She needn’t buy me a present. • We use can to express ability in the present.
• We use mustn’t and can’t to express prohibition. The baby can speak.
You mustn’t/can’t speak during the lesson. • We use could to express ability in the past.
Note: • To express obligation in the past, we use I could climb trees when I was young.
had to. • Be able to expresses ability and forms all tenses.
• To express obligation in the future, we It is mainly used in tenses where we cannot use
can.
Note: He’ll be able to play football on Saturday.
Need means that something is necessary. It is used:
• as a main verb in all tenses, in the affirmative,
negative and question form. It is followed by a full Module 4
infinitive and forms the negative and question form The verb should
with auxiliary verbs.
• as a modal verb only in the negative and question The verb should
form of the Present Simple. It is followed by a bare I/He/She/It/We/You/They should go
infinitive and forms the negative and question form AFFIRMATIVE
without auxiliary verbs. I/He/She/It/We/You/They shouldn’t
NEGATIVE go
AFFIRMATIVE Should I/he/she/it/we/you/they go?
QUESTIONS
I need to go Yes, I/he/she/it/we/you/they should.
He/She/It needs to go SHORT
We/You/They need to go ANSWERS No, I/he/she/it/we/you/they
shouldn’t.
111
19/2/2021 5:11:51 µµ
GTTTop4_Rev_SERBIA_SB_GrammRef_SERBIAN_106-117--.indd 111 19/2/2021 5:11:51 µµ
GTTTop4_Rev_SERBIA_SB_GrammRef_SERBIAN_106-117--.indd 111